Copyright © GSE ONLINE SDN BHD ( 1116968-P ) ALL RIGHTS RESERVED
WHY ANTI STATIC CARPETING FOR YOUR FACILITY ?
Sophisticated electronics such as computer are manufactured in an ESD (static controlled) environment for a very good reason: To insure reliable production and reduce failures in the finished products. These same manufacturers have worked diligently to shield your sensitive microelectronics from the damaging effects of electrostatics in the end user market, yet user induced static discharge continues to be a proven cause of computer related problems.
Minimal static discharges (below the threshold of human perception) often cause occasional (yet annoying) glitches while more powerful discharges (> 2,500 volts) wreak havoc, causing network instability, damage to micro electronics, corrupted data and lost production. The question is not IF static can damage the integrity of your electronics but WHEN. It's just not worth the risk .
ESD Mats / Static Control Matting
Static control mats are an effective method of controlling electrostatic discharge (ESD for short). Static electricity is typically generated by the contact and separation of a person's clothes against their skin. The static builds until the person touches something of a lower static potential. If uncontrolled, this immediate discharge (an event) often causes irreparable damage to sensitive micro electronics. Static control mats slow and control the esd event and allow the charge to migrate harmlessly to ground.
For many years, electronics companies have invested in static-preventive wrist straps, bins, bags, table mats, and ionizers—all in the hopes of eliminating electrostatic discharge.
Some organizations realized immediate improvements—both in yield and in reduction of field returns. Others simply found an ESD program necessary for successful solicitation and retention of contracts. Many are not sure just what they got and worse, why they got it. ESD has been recognized as a threat to electronic devices since the introduction of blasting caps and detonators to the mining industry. Numerous technical articles, awareness seminars, and preventive products are readily accessible to industry. The cause, effect, and solution to ESD is widely accepted and well documented. Why, then, is it so difficult for engineers to convince management to provide the funds essential for establishing an in-house static program? Many times, ESD-control programs do not measure up to the anticipated objectives, or even more disheartening, are completely ineffective. To a wide extent, these programs never really had a fighting chance; they were doomed from inception. A major manufacturer of computer peripherals was quite proud of its ESD program and was not shy to point out its considerable expenditure.
ESD and Anti Static Flooring Terminology
Antistatic Carpet:
The term antistatic refers to a condition where static generation is inhibited during contact and separation with a different material. In general, antistatic carpet is any carpet product that will generate less static electricity than standard carpet. Antistatic carpet is not conductive and it is not possible to ground anti-static carpet. Antistatic carpet usually contains bi-component yarns. The reason for specifying antistatic carpet is to establish a space that will be free of static shocks, or zaps. Most new antistatic carpet will prevent shocks as long as the relative humidity (RH) is above 25%. Anti static carpet should NOT be confused with conductive or ESD carpet. Antistatic is not a permanent property.
Anti Static Flooring:
The term antistatic refers to a condition where static generation is inhibited during contact and separation with a different material. Anti static flooring can either be static dissipative or static conductive.
Conductive:
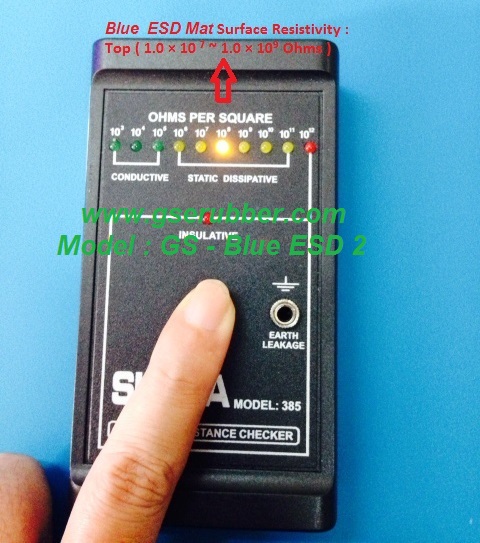
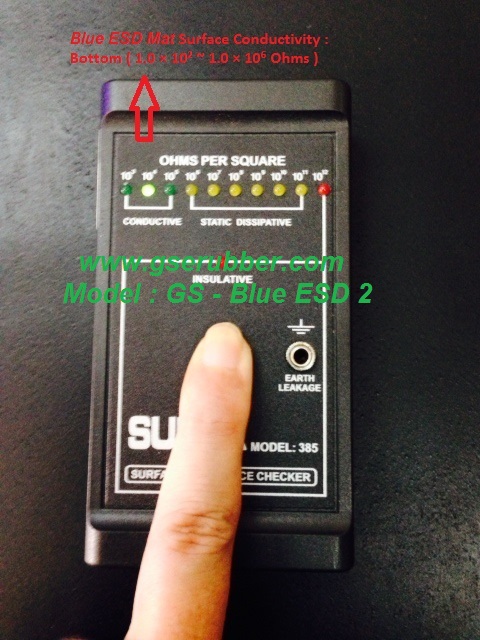
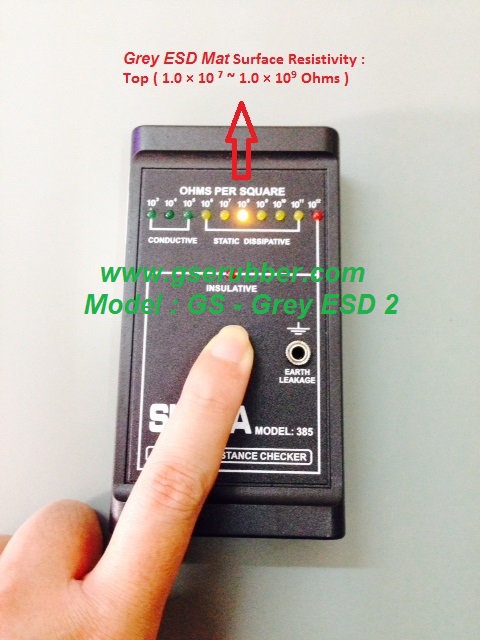
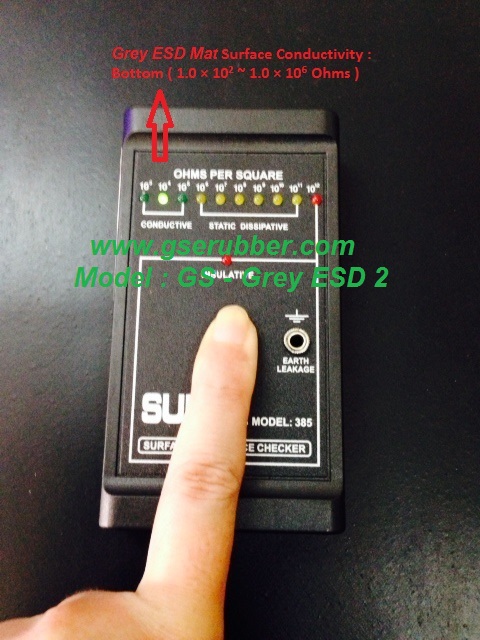
refers to the ability of a material to conduct a charge to ground and is usually indicated by an electrical resistance range measured in ohms of a minimum of 2.5 x 10⁴, ( 25,000 ohms ), to a maximum of 1.0 x 10⁶,
(1 million ohms)


Why We Need Anti - Static Material ?
Have you ever walked across a carpeted floor and gotten a shock when you touched a doorknob, table, counter, or even another person? That little shock you got was a result of static electricity. It was also many times what is needed to destroy some computer components. You see, humans can't feel a static shock until it is several thousand volts strong, but it takes less than 30 volts to damage a sensitive computer component, such as a stick of RAM or a processor. That's why computer technicians and home computer builders have to guard their computers against the deadly ravages of static electricity, as well as take steps to avoid injury to yourself. A shock that you can't even feel can seriously damage your homebuilt computer before you're even finished building it. Outstanding Protection from Static Induced Damage to Mission Critical Data, Networks, Servers and Computers